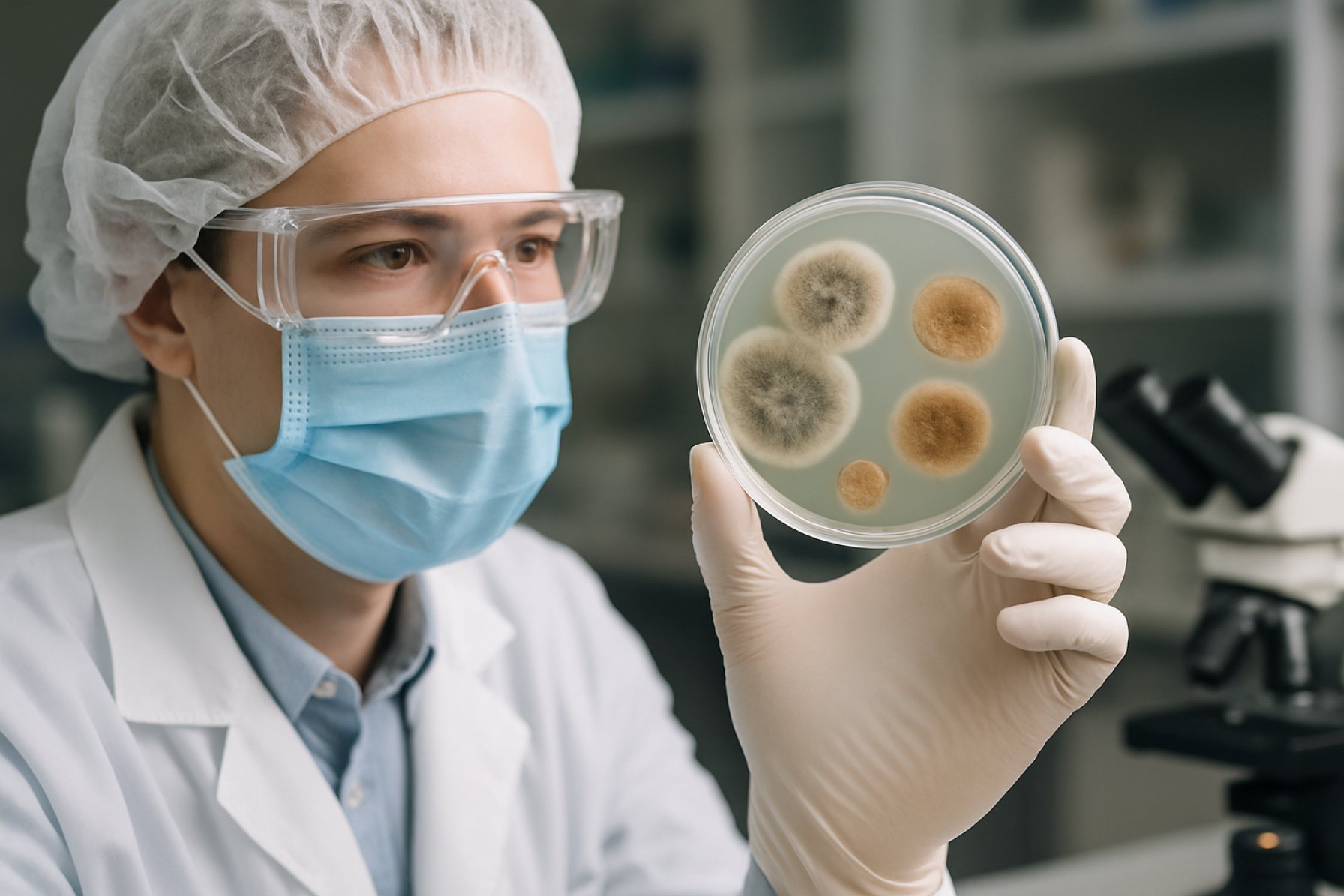
Fungal Genomics for Foodtech Market Report 2025: Unlocking Growth Through Precision Fermentation and Next-Gen Protein Solutions. Explore Market Size, Key Players, Technology Trends, and Strategic Opportunities Shaping the Industry.
- Executive Summary & Market Overview
- Key Technology Trends in Fungal Genomics for Foodtech
- Competitive Landscape and Leading Innovators
- Market Size, Growth Forecasts & CAGR Analysis (2025–2030)
- Regional Market Analysis: North America, Europe, APAC & RoW
- Challenges, Risks, and Barriers to Adoption
- Opportunities & Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
- Future Outlook: Emerging Applications and Investment Hotspots
- Sources & References
Executive Summary & Market Overview
Fungal genomics for foodtech represents a rapidly evolving intersection of biotechnology and the food industry, leveraging advanced genomic tools to unlock the potential of fungi in food production, ingredient innovation, and sustainability. As of 2025, the global market for fungal genomics in foodtech is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for alternative proteins, sustainable food sources, and novel food ingredients. Fungi, including yeasts and filamentous species, are being harnessed for their ability to produce high-value compounds, improve food safety, and enable precision fermentation processes.
The market is characterized by significant investments in research and development, with leading foodtech companies and startups utilizing next-generation sequencing, CRISPR-based genome editing, and synthetic biology to optimize fungal strains for specific applications. These applications range from the production of mycoprotein-based meat alternatives to the biosynthesis of flavor enhancers, enzymes, and functional ingredients. The adoption of fungal genomics is also facilitating the development of clean-label products and reducing reliance on traditional animal agriculture, aligning with consumer preferences for health, sustainability, and transparency.
According to Grand View Research, the global food biotechnology market, which includes fungal genomics applications, was valued at over USD 25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10-12% through 2030. The segment focused on fungal genomics is expected to outpace the broader market, fueled by breakthroughs in strain engineering and the scaling of precision fermentation platforms. Notable industry players such as Mycorena, Quorn Foods, and Nature’s Fynd are at the forefront, commercializing fungal-based proteins and ingredients for mainstream food applications.
- Europe and North America are leading regions in terms of investment and commercialization, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and strong consumer acceptance of alternative proteins.
- Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth market, driven by population growth, urbanization, and increasing awareness of sustainable food solutions.
- Key challenges include regulatory approval processes, scalability of fermentation technologies, and consumer education regarding the safety and benefits of fungal-derived foods.
In summary, fungal genomics is poised to play a transformative role in the foodtech sector in 2025, offering innovative solutions to global food security, sustainability, and nutrition challenges while attracting significant industry and investor interest.
Key Technology Trends in Fungal Genomics for Foodtech
Fungal genomics is rapidly transforming the foodtech sector, driven by advances in sequencing technologies, bioinformatics, and synthetic biology. In 2025, several key technology trends are shaping how fungi are leveraged for sustainable food production, novel ingredients, and alternative proteins.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Multi-Omics Integration: The cost and speed of NGS have improved dramatically, enabling comprehensive genomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic profiling of edible and industrially relevant fungi. This multi-omics approach allows foodtech companies to identify novel metabolic pathways, optimize strain selection, and enhance the nutritional profile of fungal-based foods. Companies like Illumina and Oxford Nanopore Technologies are at the forefront of providing sequencing platforms tailored for high-throughput fungal genomics.
- CRISPR and Precision Genome Editing: The adoption of CRISPR-Cas systems in filamentous fungi and yeast is accelerating the development of strains with improved yield, flavor, and texture. Precision editing enables the removal of undesirable genes (such as those responsible for off-flavors or allergens) and the insertion of biosynthetic pathways for novel compounds. Startups and research groups are leveraging these tools to create proprietary fungal strains for meat analogs and functional ingredients (Nature Biotechnology).
- AI-Driven Strain Optimization: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to analyze large genomic datasets, predict gene function, and model metabolic networks. This accelerates the identification of high-performing strains and the design of fermentation processes. Companies such as Ginkgo Bioworks are integrating AI with fungal genomics to streamline the development of new food products.
- Fermentation Process Engineering: Advances in bioprocess engineering, informed by genomic insights, are enabling the scale-up of fungal biomass and mycoprotein production. Genomics-guided optimization of fermentation parameters is reducing costs and improving consistency, supporting the commercialization of products like mycelium-based meat alternatives (Good Food Institute).
- Functional Ingredient Discovery: Genomic mining is uncovering new enzymes, flavors, and bioactive compounds from diverse fungal species. These discoveries are fueling the development of clean-label ingredients, natural preservatives, and health-promoting additives for the food industry (Mordor Intelligence).
Collectively, these technology trends are positioning fungal genomics as a cornerstone of innovation in foodtech, enabling more sustainable, nutritious, and diverse food solutions for 2025 and beyond.
Competitive Landscape and Leading Innovators
The competitive landscape of fungal genomics for foodtech in 2025 is characterized by a dynamic mix of established biotechnology firms, food industry giants, and agile startups leveraging advanced genomic tools to unlock the potential of fungi in food innovation. The sector is witnessing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable protein alternatives, functional ingredients, and novel flavors, as well as the need for resilient food production systems.
Key players in this space include Novozymes, which has invested heavily in fungal strain development for enzyme production and alternative protein applications, and Mycorena, a Swedish startup specializing in mycoprotein-based food products using proprietary fungal genomics platforms. Quorn Foods, a pioneer in mycoprotein foods, continues to innovate by optimizing Fusarium venenatum strains through genomic selection and metabolic engineering.
Emerging innovators such as Ecovative are expanding the use of fungal genomics beyond food into packaging and materials, but their subsidiary MyForest Foods is focused on developing whole-cut meat alternatives from mycelium, utilizing genomic insights to enhance texture and nutritional profiles. EniferBio in Finland is commercializing PEKILO® mycoprotein, leveraging advanced genomics to improve yield and scalability.
The competitive edge in this market is increasingly defined by proprietary genomic databases, high-throughput sequencing capabilities, and bioinformatics platforms that enable rapid strain improvement and functional gene discovery. Companies are forming strategic partnerships with academic institutions and technology providers to accelerate R&D. For example, Ginkgo Bioworks collaborates with foodtech startups to provide custom fungal engineering services, while Merck KGaA offers genomic tools and reagents tailored for fungal research.
- Investment activity is robust, with venture capital flowing into startups focused on precision fermentation and mycoprotein production.
- Intellectual property portfolios around engineered fungal strains and fermentation processes are becoming a key differentiator.
- Regulatory approvals and consumer acceptance remain critical hurdles, but leading innovators are proactively engaging with regulators and launching pilot products in select markets.
As the field matures, the competitive landscape is expected to consolidate around those with the strongest genomic toolkits, scalable production platforms, and the ability to deliver differentiated, sustainable food products at commercial scale.
Market Size, Growth Forecasts & CAGR Analysis (2025–2030)
The global market for fungal genomics in foodtech is poised for robust expansion between 2025 and 2030, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable food production, alternative proteins, and advanced fermentation technologies. According to projections from Grand View Research and MarketsandMarkets, the broader genomics market is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 15–18% during this period, with the fungal genomics segment in foodtech anticipated to outpace this average due to its specialized applications in food innovation.
In 2025, the fungal genomics for foodtech market is estimated to be valued at around USD 350–400 million, encompassing applications such as strain improvement, enzyme production, precision fermentation, and the development of novel food ingredients. By 2030, the market size is projected to reach USD 800 million to USD 1 billion, reflecting a CAGR in the range of 16–18% over the forecast period. This growth is underpinned by the rapid adoption of next-generation sequencing (NGS), CRISPR-based genome editing, and bioinformatics platforms tailored for fungal species relevant to food production.
Key drivers of this market expansion include:
- Rising investments in alternative protein sources, particularly mycoprotein and fungal-derived ingredients, by major foodtech companies and venture capital firms (Good Food Institute).
- Increasing collaborations between genomics technology providers and food manufacturers to optimize fermentation processes and enhance product yields (SynBioBeta).
- Growing consumer demand for clean-label, sustainable, and functional foods, which is accelerating the adoption of fungal genomics for ingredient innovation (Euromonitor International).
Regionally, North America and Europe are expected to dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of global revenues by 2030, due to strong R&D ecosystems and supportive regulatory frameworks. However, Asia-Pacific is projected to exhibit the fastest CAGR, driven by expanding foodtech startups and government initiatives in biotechnology (Frost & Sullivan).
Overall, the fungal genomics for foodtech market is set for dynamic growth, with technological advancements and strategic partnerships shaping its trajectory through 2030.
Regional Market Analysis: North America, Europe, APAC & RoW
The global fungal genomics market for foodtech is experiencing dynamic growth, with regional trends shaped by regulatory environments, R&D investments, and the maturity of food innovation ecosystems. In 2025, North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific (APAC), and the Rest of the World (RoW) each present distinct opportunities and challenges for stakeholders in fungal genomics applied to food technology.
North America remains a frontrunner, driven by robust investments in biotechnology and a strong presence of foodtech startups. The United States, in particular, benefits from advanced genomic infrastructure and supportive regulatory frameworks, fostering collaborations between academia and industry. Companies such as Ginkgo Bioworks and MycoTechnology are leveraging fungal genomics to develop novel ingredients and alternative proteins, with the region accounting for a significant share of global patent filings and venture capital inflows in 2025. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) progressive stance on novel food ingredients further accelerates commercialization.
Europe is characterized by a strong focus on sustainability and regulatory rigor. The European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy and the European Food Safety Authority’s (EFSA) guidelines on novel foods have spurred investments in fungal genomics for clean-label and plant-based food solutions. Countries like the Netherlands, Germany, and the UK are home to leading research institutions and startups, such as Nutreco and Quorn Foods, which are integrating fungal genomics to enhance product quality and traceability. However, the region’s stringent approval processes can lengthen time-to-market for new products.
- APAC is emerging as a high-growth region, propelled by rising consumer demand for alternative proteins and functional foods. China, Japan, and Singapore are investing heavily in foodtech R&D, with government-backed initiatives supporting startups and multinational collaborations. Singapore’s regulatory agility, exemplified by the Singapore Food Agency’s (SFA) rapid approval of novel foods, positions it as a regional hub for fungal genomics innovation (Singapore Food Agency).
- Rest of the World (RoW) includes Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, where adoption is nascent but growing. Brazil and Israel are notable for their investments in agri-biotech and food innovation, with local players exploring fungal genomics for sustainable food production (Embrapa, Startup Nation Central).
Overall, while North America and Europe lead in technology and regulatory frameworks, APAC’s rapid adoption and RoW’s emerging initiatives are expanding the global footprint of fungal genomics in foodtech for 2025.
Challenges, Risks, and Barriers to Adoption
The adoption of fungal genomics in foodtech faces a complex array of challenges, risks, and barriers that could impede its widespread integration by 2025. One of the primary hurdles is the regulatory uncertainty surrounding genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and genome-edited fungi. Regulatory frameworks differ significantly across regions, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintaining stringent approval processes, while the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has a more flexible, case-by-case approach. This lack of harmonization complicates global commercialization and increases compliance costs for foodtech companies.
Intellectual property (IP) concerns also present a significant barrier. The rapid pace of innovation in fungal genomics has led to a crowded patent landscape, making freedom-to-operate analyses both costly and time-consuming. Disputes over proprietary strains, gene-editing techniques, and bioinformatics tools can delay product launches and deter investment, as highlighted by recent legal cases in the biotech sector (World Intellectual Property Organization).
Technical challenges persist as well. Fungal genomes are often complex, with high levels of genetic redundancy and poorly annotated regions, making precise editing and trait prediction difficult. The scalability of fermentation processes using novel fungal strains remains a bottleneck, with issues such as contamination, yield variability, and process optimization requiring significant R&D investment (Nature Biotechnology).
Consumer acceptance is another critical risk. Despite the sustainability and nutritional benefits of fungal-derived foods, public perception of GMOs and synthetic biology remains mixed. Misinformation and lack of transparency can fuel skepticism, particularly in markets with strong organic or natural food movements. Companies must invest in education and transparent labeling to build trust (International Food Policy Research Institute).
Finally, supply chain integration poses logistical barriers. Sourcing, scaling, and distributing fungal-based ingredients require new infrastructure and partnerships, especially for startups lacking established networks. The need for cold-chain logistics, specialized bioreactors, and quality control systems adds to operational complexity and cost (McKinsey & Company).
In summary, while fungal genomics holds transformative potential for foodtech, overcoming these multifaceted challenges will require coordinated efforts across regulatory, technical, commercial, and societal domains.
Opportunities & Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
The intersection of fungal genomics and foodtech presents a dynamic landscape of opportunities for stakeholders in 2025. As the global demand for sustainable, nutritious, and novel food products intensifies, leveraging advanced genomic tools to harness the potential of fungi is becoming a strategic imperative. Key opportunities and recommendations for stakeholders are outlined below:
- Alternative Protein Development: Fungal genomics enables the identification and optimization of high-protein fungal strains, such as mycoprotein-producing Quorn Foods and other filamentous fungi. Stakeholders should invest in R&D partnerships to accelerate the discovery of strains with superior nutritional profiles and scalable fermentation characteristics.
- Functional Ingredient Innovation: Genomic insights facilitate the engineering of fungi to produce bioactive compounds, flavors, and texturizers. Foodtech companies can collaborate with genomics firms to develop proprietary ingredients that enhance product differentiation and health benefits, as seen in the work of MycoTechnology.
- Precision Fermentation Platforms: The application of CRISPR and other gene-editing tools to fungal genomes allows for the tailored production of enzymes, vitamins, and specialty lipids. Strategic investment in precision fermentation infrastructure can position stakeholders at the forefront of the rapidly growing alternative food ingredient market, projected to reach $36.3 billion by 2030 (Boston Consulting Group).
- Sustainability and Circular Economy: Fungi’s ability to upcycle agricultural waste into high-value food products aligns with global sustainability goals. Stakeholders should explore partnerships with agri-food supply chains to implement circular models, reducing waste and carbon footprints (Ellen MacArthur Foundation).
- Regulatory and Consumer Engagement: As regulatory frameworks for novel foods evolve, proactive engagement with authorities and transparent communication with consumers will be critical. Stakeholders should participate in industry consortia and public education initiatives to build trust and facilitate market entry (FoodNavigator).
In summary, stakeholders in fungal genomics for foodtech should prioritize collaborative innovation, invest in scalable bioprocessing, and engage with regulatory and consumer landscapes. These strategies will unlock new revenue streams and drive the adoption of fungi-derived foods in mainstream markets.
Future Outlook: Emerging Applications and Investment Hotspots
The future outlook for fungal genomics in foodtech is marked by rapid innovation, expanding applications, and increasing investment interest as the sector matures into a critical pillar of sustainable food production. By 2025, the convergence of advanced sequencing technologies, synthetic biology, and precision fermentation is expected to unlock new frontiers in the use of fungi for food ingredients, alternative proteins, and functional foods.
Emerging applications are particularly focused on the development of mycoprotein-based meat alternatives, novel flavor and texture enhancers, and bioactive compounds for health-promoting foods. Companies such as Quorn Foods and Nature’s Fynd are leveraging fungal genomics to optimize strains for higher yield, improved nutritional profiles, and tailored sensory attributes. The ability to engineer fungal genomes with precision is also enabling the production of specialty ingredients, such as dairy proteins and fats, without the need for animal agriculture, as demonstrated by startups like Perfect Day.
Investment hotspots are emerging in regions with robust biotech ecosystems and supportive regulatory frameworks. North America and Europe continue to lead, with significant venture capital flowing into companies focused on fermentation-derived proteins and ingredients. According to The Good Food Institute, global investment in fermentation-enabled alternative proteins reached $1.7 billion in 2023, with a strong upward trajectory projected through 2025. Asia-Pacific is also gaining momentum, driven by rising demand for sustainable protein sources and government-backed innovation hubs.
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with fungal genomics is expected to accelerate strain discovery and optimization, reducing time-to-market for new food products. Additionally, partnerships between foodtech startups, established food manufacturers, and research institutions are likely to proliferate, fostering knowledge transfer and scaling capabilities. Regulatory clarity around novel food approvals, particularly in the EU and US, will further catalyze commercialization efforts.
In summary, the future of fungal genomics in foodtech is characterized by a dynamic landscape of scientific breakthroughs, expanding product portfolios, and robust investment activity. As consumer demand for sustainable, nutritious, and innovative foods grows, fungal genomics is poised to play a transformative role in shaping the next generation of food systems.
Sources & References
- Grand View Research
- Mycorena
- Quorn Foods
- Illumina
- Nature Biotechnology
- Ginkgo Bioworks
- Mordor Intelligence
- Quorn Foods
- Ecovative
- MarketsandMarkets
- SynBioBeta
- Euromonitor International
- Frost & Sullivan
- Nutreco
- Embrapa
- Startup Nation Central
- European Food Safety Authority
- World Intellectual Property Organization
- International Food Policy Research Institute
- McKinsey & Company
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation
- FoodNavigator
- Perfect Day